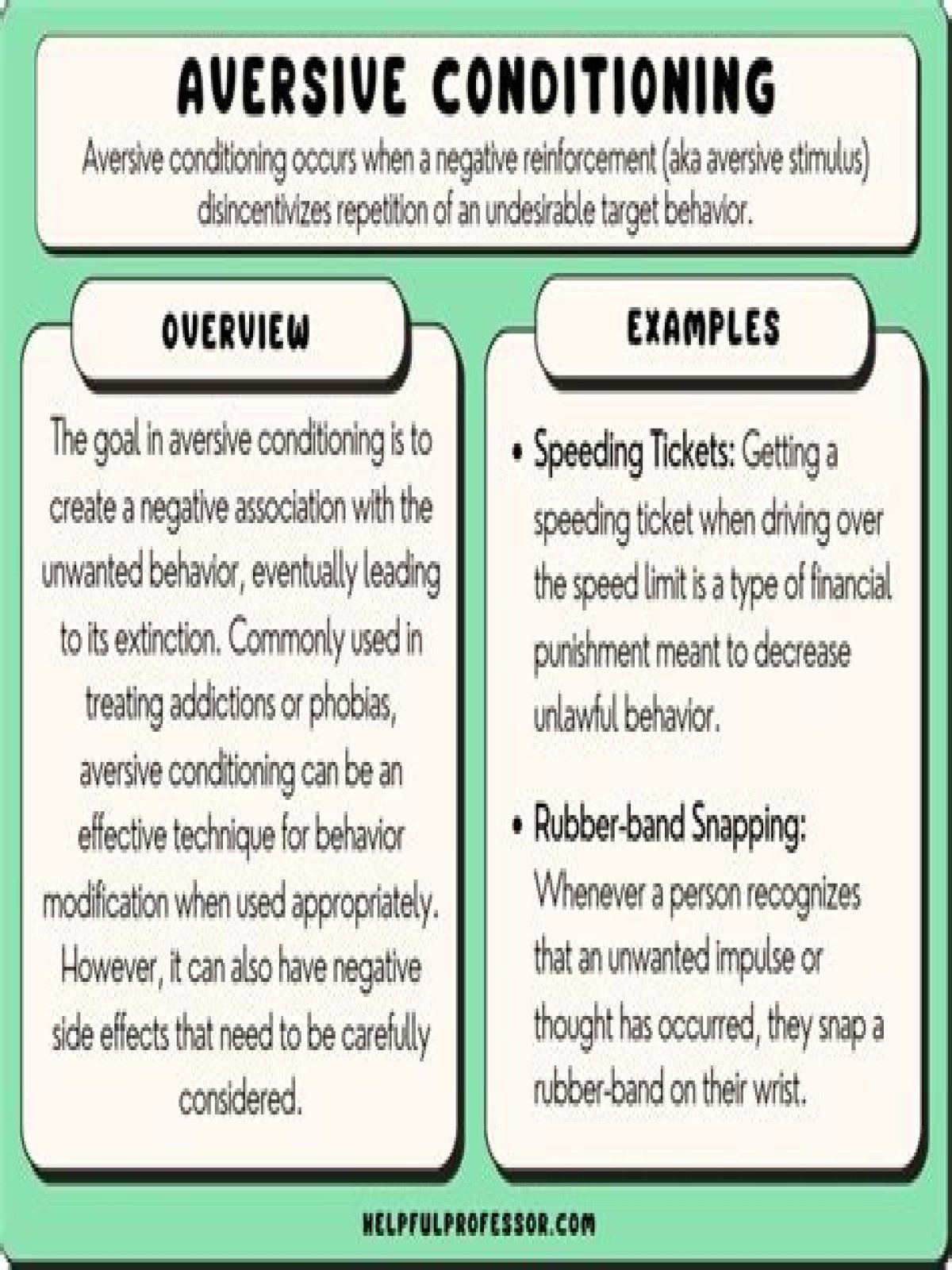
aversive conditioning
Aversion therapy, sometimes called aversive therapy or aversive conditioning, is used to help a person give up a behavior or habit by having them associate it with something unpleasant. Aversion therapy is most known for treating people with addictive behaviors, like those found in alcohol use disorder.
What is an example of aversive?
Examples include extreme heat or cold, bitter flavors, electric shocks, loud noises and pain. Aversives can be applied naturally (such as touching a hot stove) or in a contrived manner (such as during torture or behavior modification).
What techniques are used in aversive conditioning?
Aversive techniques have included administering shocks to a person’s genitals or inducing a person to vomit when he or she is stimulated by sexualized images of members of the same sex.
What is the meaning of aversive therapy?
aversion therapy, psychotherapy designed to cause a patient to reduce or avoid an undesirable behaviour pattern by conditioning the person to associate the behaviour with an undesirable stimulus. The chief stimuli used in the therapy are electrical, chemical, or imagined aversive situations.
What drugs are used in aversion therapy?
While a number of drugs have been employed in chemical aversion therapy, the three most commonly used are emetine, apomorphine, and lithium.
Why is aversion therapy unethical?
Because aversion therapy involves the use of unpleasant stimuli, it’s quite controversial. Some therapists think it’s unethical because it uses punishment as a therapeutic tool. Any punishment may lead to feelings of shame and guilt, which in turn may impact your mental health.
Is aversive conditioning classical conditioning?
In classical conditioning, an initially neutral stimulus (conditioned stimulus, CS) becomes associated with a biologically salient event (unconditioned stimulus, US), which might be pain (aversive conditioning) or food (appetitive conditioning).
What’s an example of classical conditioning?
For example, imagine that you are conditioning a dog to salivate in response to the sound of a bell. You repeatedly pair the presentation of food with the sound of the bell. You can say the response has been acquired as soon as the dog begins to salivate in response to the bell tone.
Is aversive conditioning classical conditioning or operant?
aversive conditioning learning in which punishment or other unpleasant stimulation is used to associate negative feelings with an undesirable response. classical conditioning conditioning (def. 2).
When was aversion therapy first used?
Various forms of aversion therapy have been used in the treatment of addiction to alcohol and other drugs since 1932 (discussed in Principles of Addiction Medicine, Chapter 8, published by the American Society of Addiction Medicine in 2003).
Where is aversion therapy used?
Aversion therapy is most commonly used to treat drug and alcohol addictions. 3 A subtle form of this technique is often used as a self-help strategy for minor behavior issues. In such cases, people may wear an elastic band around the wrist.
How is aversion therapy based on classical conditioning?
Aversion therapy is based on classical conditioning. According to learning theory, two stimuli become associated when they occur frequently together (pairing). For example, in addiction, the drug, alcohol or behavior in the case of gambling becomes associated with pleasure and high arousal.